Introduction of Is Matter Around Us Pure
This chapter Is Matter Around Us Pure is an explanation of the first chapter in Ncert chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings because it is the next main lesson of class 9.
Mixtures
- Constitutes more than one kind of pure substance.
For example, milk is a mixture of water and fat protein, etc.
to know about the the chemical change click here.
Homogenus mixture
A mixture which has uniform composition is homogeneous mixture.
solution
A homogenous mixture of two or more substances is solution.
It has solvent and a solute as componants.
Particles are of small size and do scatter a beam of light passing through the solution.

In Another case
Formula for concentration of solution is
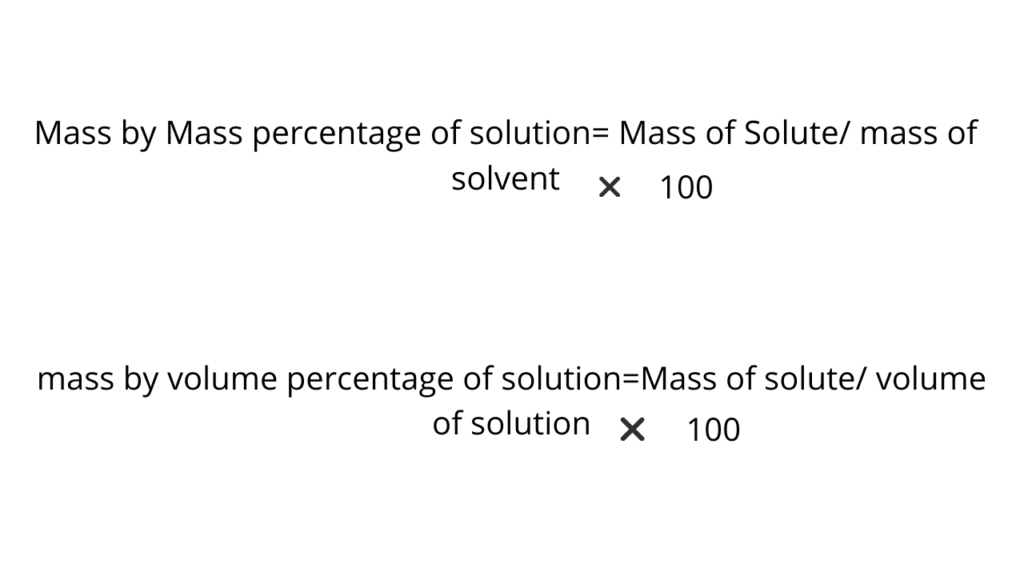
Heterogeneous mixture
So the mixture which there is no uniform composition is heterogeneous mixture.
Suspention
It is the heterogeneous mixture in which the solid particles do not dissolve between suspended throughout the bulk of the medium.
Colloid
- It is a heterogeneous mixture but it look like homogeneous mixture.
- The scattering of light by colloidal particles is tyndall effect.
- Special process is used for separating components of mixture because example evaporation, certification, separating funnel ,sublimation chromatography, distillation, crystallization etc.
Evaporation
So evaporation is a method that can be used two separate have volatile components from the non-volatile components of a mixture.
Centrifugation
The method is used to separate components that have a difference in densities.
Seperating funnel
So It is based upon the principle that immiscible liquids separate out into layers depending on their densities.
chromotography
Seperation of mixture into components and also to seperate various substance that make mixture.
distillation
Converts a liquid to vapour, then condenses back into the liquid form.
Crystallisation
It is the process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals from the solution.
Also in physical changes only physical properties of substance changes and main chemical changes one substance reacts with another substance to undergo a change in chemical composition.
